Install Redis Enterprise Edition on OpenShift
Choosing Redis Enterprise allows you to use an operator and automate the setup and management of the Redis Cluster. This is not to be overlooked if your applications require an extremely reliable and resilient cache in an on-prem environment, which also reduces maintenance costs.
- Install Redis Enterprise Edition on OpenShift
Hardware and Software Requirements
Before starting, it is good to remember a few requirements; however, it is advisable to check the official documentation because evolution is rapid:
- Kubernetes cluster version respect support matrix
- Storage Class for persistent volumes;
- Minimum resources for install a Redis Cluster;
- (optional) worker node in 3 different availability zone;
Architecture
The operator Redis Enterprise provides custom resource definitions (CRDs) to create and manage the Redis Enterprise Cluster (REC) and the Redis Enterprise databases (REDB). The operator is namespaced, so resources must be created within the same namespace where it works.
For production environments, it is recommended to create clusters of at least three Redis nodes and deploy them on the OpenShift cluster with anti-affinity policies. The reliability of the service for our application moves into the internal Redis logics, for each Redis database, it is required to specify the number of slave shards and the recovery behaviour in the event of an interruption of the master shard.
A very interesting functionality offered by Redis Enterprise is ‘Rack-zone awareness’. When activating this function in a cluster, a zone ID is automatically assigned to each Redis node. This ID is used to map the node to a logical zone. The cluster can then ensure that the master shard and corresponding replication shards are located on OpenShift nodes in different zones.
Preparation
Create namespace and Security Context Constraint
To successfully start the operator in OpenShift, you need to create a security context constraint (SCC). The Redis documentation provides the specific SCC that should be applied in this case.
- Create a new project
oc new-project redis. - Download o create scc.yaml file.
- Apply the file to install the security context constraint
oc apply -f scc.yaml.
# scc.yaml
apiVersion: security.openshift.io/v1
kind: SecurityContextConstraints
metadata:
name: redis-enterprise-scc-v2
annotations:
kubernetes.io/description: redis-enterprise-scc is the minimal SCC needed to run Redis Enterprise nodes on Kubernetes. It provides the same features as restricted-v2 SCC, but allows pods to enable the SYS_RESOURCE capability, which is required by Redis Enterprise nodes to manage file descriptor limits and OOM scores for database shards. Additionally, it requires pods to run as UID/GID 1001, which are the UID/GID used within the Redis Enterprise node containers.
allowedCapabilities:
- SYS_RESOURCE
allowHostDirVolumePlugin: false
allowHostIPC: false
allowHostNetwork: false
allowHostPID: false
allowHostPorts: false
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
allowPrivilegedContainer: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
runAsUser:
type: MustRunAs
uid: 1001
fsGroup:
type: MustRunAs
ranges:
- min: 1001
max: 1001
seLinuxContext:
type: MustRunAs
seccompProfiles:
- runtime/default
supplementalGroups:
type: RunAsAny
Define ResourcesQuota and LimitRange
In kubernetes environments, it is always recommended to configure the available resource limits for each namespace; this approach allows you to keep track of the resources used and available on your cluster.
Below is an example of ResourceQuota and LimitRange to enable the creation of a Redis Enterprise cluster of 3 nodes.
# resourceQuota.yaml
kind: ResourceQuota
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: default-quota
namespace: redis
spec:
hard:
limits.cpu: '12'
limits.memory: 16Gi
requests.cpu: '12'
requests.memory: 16Gi
requests.storage: 100Gi
# limitRange.yaml
kind: LimitRange
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: default-resource-limits
namespace: redis
spec:
limits:
- type: Container
max:
cpu: '4'
memory: 4Gi
default:
cpu: 250m
memory: 500Mi
defaultRequest:
cpu: 250m
memory: 500Mi
oc apply -f limitRange.yaml -f resourceQuota.yaml
OpenShift configurations to use Rack-zone awareness
To use this function, OpenShift nodes must have a label identifying their position in relation to the availability zones of the datacenter. If we do not already have a label identifying the AZ to which we belong, we can use e.g. “topology.kubernetes.io/zone”:
oc label node lab-worker-01 topology.kubernetes.io/zone=dc1-az1
oc label node lab-worker-02 topology.kubernetes.io/zone=dc1-az2
oc label node lab-worker-03 topology.kubernetes.io/zone=dc1-az3
The Redis Enterprise operator also needs a customRole to be able to identify topology.kubernetes.io/zone labels from OpenShift nodes in order to be able to use the ‘rack awareness’ capability:
# customRole.yaml
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: redis-enterprise-operator
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "watch"]
# clusterRoleBinding.yaml
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: redis-enterprise-operator
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
namespace: redis
name: redis-enterprise-operator
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: redis-enterprise-operator
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
oc apply -f customRole.yaml -f clusterRoleBinding.yaml
Install Redis Enterprise Operator
Now, you can install the operator with the OpenShift console or from the command line by applying some manifest.
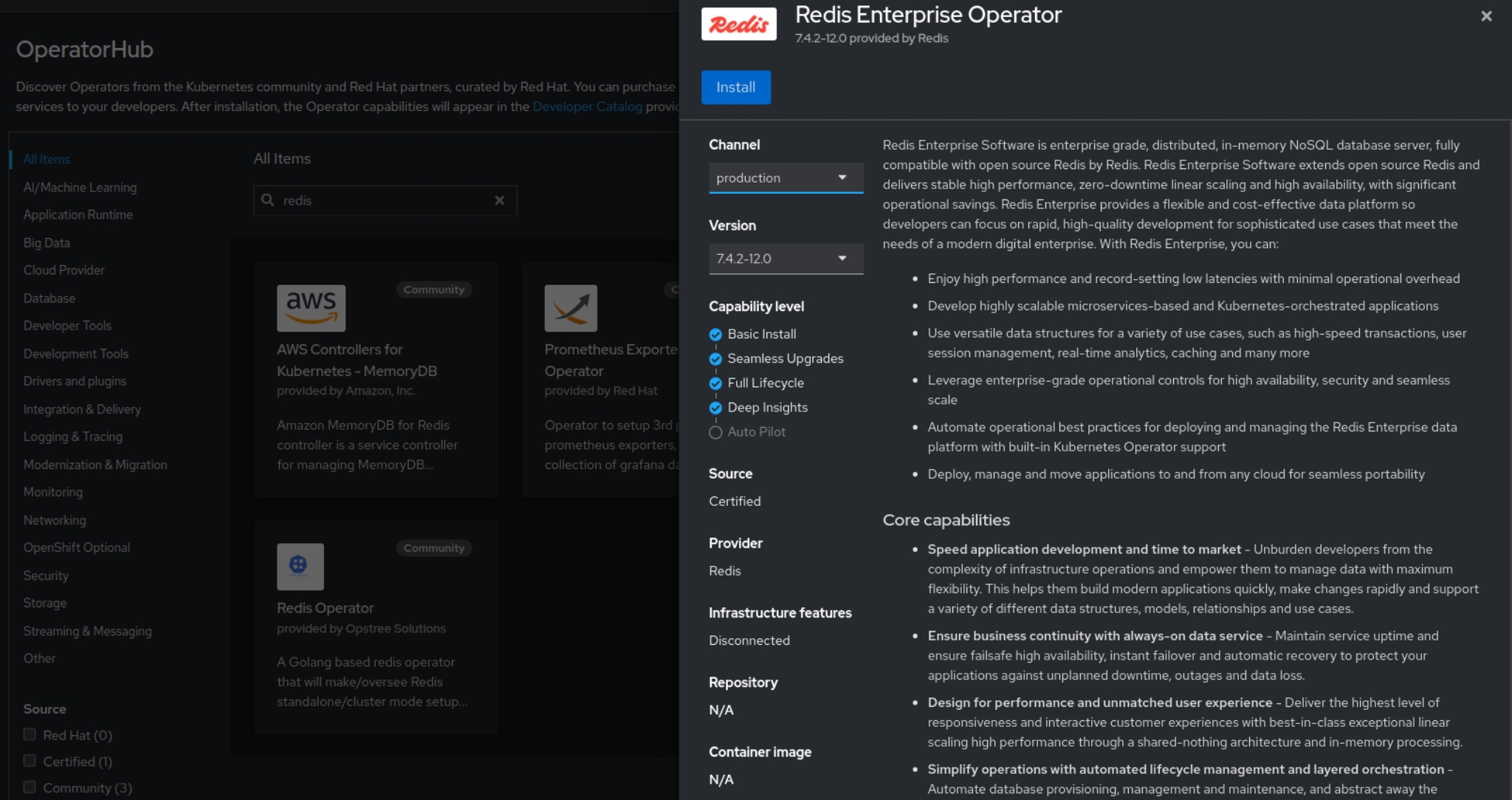
Install via OpenShift Console
- Log in to the OpenShift console
- Click on Operators > OperatorHub on the left menu
- Search Redis Enterprise Operator
- Click on Redis Enterprise Operator, select Manual as Update Approval for production
- Click on Install
Install via Manifest
- Log in with oc client
- Select namespace
- Copy and apply this manifest
# subscription.yaml
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: redis-enterprise-operator-cert
namespace: redis
spec:
channel: 7.4.6
installPlanApproval: Manual
name: redis-enterprise-operator-cert
source: certified-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
startingCSV: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.2.4-12.6
oc apply -f subscription.yaml
- Approve the install plan
oc get installplan -n redis
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED
install-ar21g redis-enterprise-operator.v7.2.4-12.6 Manual false
Approve the installation of the operator by updating the approved field of the InstallPlan:
oc patch installplan install-ar21g --namespace redis --type merge --patch '{"spec":{"approved":true}}'
Tips: Tuning operator resources 🐑
The Redis Operator pod is scheduled by default with a CPU limit of 4Gi. For development environments, it may be necessary to apply this tuning to reduce the CPU limit:
# subscription.yaml
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: redis-enterprise-operator-cert
namespace: redis
spec:
[...]
config:
resources:
limits:
cpu: 1
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 256Mi
Define Redis Enterprise Cluster (REC)
The creation of a cluster requires the definition of a CRD called RedisEnterpriseCluster, this is a very articulated object for which it is advisable to consult the documentation for more details, here only the descriptions of the fields used for this usecase will be given.
The operator by default generates self-signed certificates for the display of services, the CRD provides the possibility during creation of being able to insert its own certificates issued by the CA. The services for which you can configure your own service are: [ proxy | api | cm | syncer | metrics_exporter ].
It is advisable to change at least the “proxy” and “cm” services with your own wildcard certificate as they will be exposed via an OpenShift route. The ‘cm’ for the Redis administration console and the ‘proxy’ for external client connections.
oc create secret generic proxy-certificate --from-file=certificate=crt.pem --from-file=key=key.pem --from-literal=name=proxy -n redis
oc create secret generic cm-certificate --from-file=certificate=crt.pem --from-file=key=key.pem --from-literal=name=cm -n redis
- Definition of REC:
# redis-enterprise-cluster.yaml
kind: RedisEnterpriseCluster
apiVersion: app.redislabs.com/v1
metadata:
name: rec
namespace: redis
spec:
nodes: 3
persistentSpec:
enabled: true
storageClassName: <changeme> #storage class name
volumeSize: 10Gi
uiServiceType: ClusterIP
bootstrapperImageSpec:
repository: registry.connect.redhat.com/redislabs/redis-enterprise-operator
redisEnterpriseServicesRiggerImageSpec:
repository: registry.connect.redhat.com/redislabs/services-manager
redisEnterpriseImageSpec:
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
repository: registry.connect.redhat.com/redislabs/redis-enterprise
redisEnterpriseNodeResources:
limits:
cpu: '1'
memory: 4Gi
requests:
cpu: '1'
memory: 4Gi
redisEnterpriseAdditionalPodSpecAttributes:
topologySpreadConstraints:
- labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: redis-enterprise
redis.io/role: node
maxSkew: 1
topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone
whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule
rackAwarenessNodeLabel: topology.kubernetes.io/zone
username: admin
certificates:
cmCertificateSecretName: cm-certificate
proxyCertificateSecretName: proxy-certificate
After the creation of the Redis cluster this is the situation:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
rec-0 2/2 Running 0 1m
rec-1 2/2 Running 0 1m
rec-2 2/2 Running 0 1m
rec-services-rigger-8bfd58796-n2jlc 1/1 Running 0 1m
redis-enterprise-operator-6b99ccb647-j5fc5 2/2 Running 0 8m
Expose Administration Console
Redis Enterprise provides a user administration console that must be exposed via the OpenShift route, create the following manifest in order to reach the GUI:
# admin-console.yaml
apiVersion: route.openshift.io/v1
kind: Route
metadata:
labels:
app: redis-enterprise
redis.io/cluster: rec
name: console
namespace: redis
spec:
host: console-redis.apps.<clustername>.<basedomain> #cluster name and basedomain
port:
targetPort: ui
tls:
termination: passthrough
to:
kind: Service
name: rec-ui
weight: 100
wildcardPolicy: None
Info
It is important to note that the SSL termination is passthrought because the Redis pod exposes the gui service in SSL.
Open the browser and copy the route url:
To log in, retrieve the credentials of the admin user:
oc get secret rec -n redis --template={{.data.password}} | base64 -d
Define Redis Enterprise Database (REDB)
You can find out how to use Redis Enterprise in kubernetes/openshift in the Install Redis Enterprise Edition on OpenShift (part 2)



